By Iñaki Senar Zuñiga, paper converting sales director, MTorres
In the ever-evolving landscape of the packaging-material industry, the advent of “Digital Twin” technology has ushered in a new era of efficiency and precision. By enabling “virtual behavior” testing of new substrates on equipment, this revolutionary technology has significantly reduced the reliance on real machinery, personnel and material, thereby leading to substantial cost and time savings.
Introduction
Digital Twin technology allows companies to simulate real production situations on a digital model, providing valuable insights into how the material will behave. This not only optimizes production processes but also ensures they are more efficient and cost-effective. This article delves into the transformative impact of Digital Twin technology on the packaging industry, particularly in the context of web-tension variation control.
From addressing the challenges and opportunities in the current uncertain context to the key aspects of web handling and the role of Digital Twin technology in wrinkle elimination, this article provides a comprehensive overview of the subject.
Challenges and opportunities permeate web-handling machinery manufacturing landscape
Amid an environment of uncertainty, web-handling system manufacturers are grappling with myriad new challenges. New process requirements continually are emerging, necessitating adaptability and innovation. Manufacturers must stay abreast of these evolving demands to ensure their machinery remains relevant and effective. This constant need for adaptation can lead to costly redesigns, upgrades and implementation, further straining resources. Moreover, downtime, often resulting from supply-chain problems or machinery malfunctions, poses a significant challenge. Such interruptions can lead to substantial financial losses and disrupt the smooth functioning of operations.
In this context, flexibility and efficiency have emerged as key strategies. Manufacturers and converted-material producers must be flexible enough to adapt to changing requirements and efficient in their operations to minimize downtime and manage costs.
Looking ahead, sustainability presents a formidable challenge. The advent of new substrates and increasing demand for sustainable practices necessitate a shift in approach. Manufacturers now must consider the environmental impact of their operations and strive to incorporate sustainable practices.
However, every challenge brings with it an opportunity. In this case, digitalization emerges as a great prospect. Integration of new technologies and tools can help manufacturers navigate these challenges. Digitalization can streamline processes, improve efficiency and open up new avenues for innovation.
How Digital Twins could be used: Web-handling tension-control system design
Let’s focus on the critical aspects of web-handling control in high-demand processes.
Continuous web supply is a fundamental requirement in any web-handling process. Ensuring a steady, uninterrupted supply of web material is crucial for maintaining efficiency and productivity of the process. Here, splice technology plays a pivotal role. It allows for seamless joining of the end of an expiring web roll to the beginning of a new one, ensuring a continuous web supply without having to stop the process.
Next, we delve into web-tension control. Accurate control of web tension is vital for maintaining quality and consistency of the final product. Inaccurate tension control can lead to defects such as wrinkles, web breaks or misalignment. Therefore, implementing robust web tension-control mechanisms, including web-guiding technologies related to rollers or active elements, not just edge guides, is essential for any web-handling process.
Digital development approach for adopting a new tension-control system
The development of specific equipment or solutions for better web-handling control could be done by a meticulous digital approach, leveraging advanced modeling and simulation tools to iterate and optimize design elements. Central to this approach is the use of modeling tools such as Mechanical System Modeling (MSM), which involves creating a detailed simulation model to replicate the behavior of mechanical systems, and simulation platforms. These tools let engineers accurately replicate real-world conditions, assess performance and refine design parameters.
Digital Twin technology is revolutionizing the packaging industry by enabling “virtual behavior” testing of new substrates on equipment. Instead of using real machinery, personnel and material, these tests are conducted on digital models, significantly cutting costs and time. This technology allows companies to obtain results on how the material will behave in real production situations by conducting tests on a digital model. In summary, Digital Twin technology provides a valuable tool for testing and optimizing production processes in a more efficient and cost-effective manner.
Cost and time-to-market
According to a study, manufacturing companies that use digital technologies to transform their operations have reduced costs between 5% and 30%, while also increasing productivity between 5% and 40% (see Figure 1).
Cost reductions: Digital Twin technology allows for virtual prototyping and simulation of product designs, enabling engineers to identify and rectify potential issues before physical prototypes are built. By minimizing the need for costly physical prototypes and iterative testing, companies can realize substantial cost savings in product development. Additionally, the ability to simulate various design configurations and manufacturing processes enables optimization for cost-efficiency without sacrificing performance or quality.
Increased productivity: Digital Twins provide a virtual representation of the product and its manufacturing processes, allowing for real-time monitoring, analysis and optimization of production workflows. By leveraging predictive analytics and machine-learning algorithms, companies can identify inefficiencies, streamline processes and minimize downtime. Furthermore, Digital Twins facilitate continuous improvement through iterative design iterations, enabling companies to adapt quickly to changing market demands and customer requirements, thereby enhancing overall productivity.
A practical example: Wrinkle elimination
Design, manufacturing and integration of a specific Tension-Control System for tension control and the avoidance of problems and quality issues in real production processes, such as wrinkles.
Digital Twin allows an Iterative Design Process: The iterative design process encompasses a series of systematic evaluations and refinements to optimize performance and mitigate potential challenges. Key design elements, including web tension-control mechanisms, dancer positions and roller configurations, undergo extensive testing to identify the most effective configurations. Each design iteration is informed by empirical data and computational simulations, facilitating informed decision-making and rapid optimization.
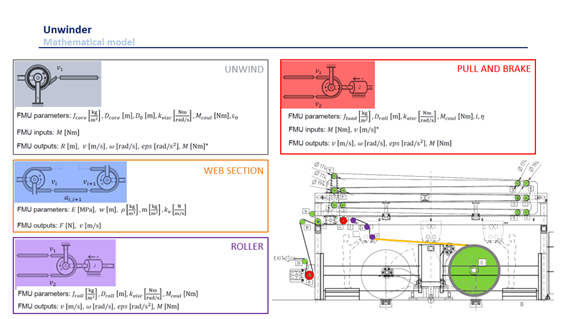
Phase One of the process is to create a Mathematical Model of the equipment/process where the new system or production test is aimed to be implemented (see Figure 2).
Phase Two is establishing the starting point with measurement and data collection of the process as it is right now. For the design of a new Tension-Control System, it is necessary to know the current tension variations over the process and to identify key elements that most affect the process (see Figure 3).
Phase Three is creating iterations over different machine configurations, designs or changes into the process. In this phase, the engineering team creates different possible solutions that are tested “instantly” by the Digital Twin. Every different test provides all the needed data to compare the test result with the already determined “starting position.”
The result of the Iterative Design Process (Stage Three) incorporates several technical innovations aimed at enhancing web-handling efficiency and performance (see Figure 4). These include:
- Advanced web tension-control algorithms leveraging real-time sensor data and PLC control systems
- Integration of sophisticated web-guiding technologies to ensure precise alignment and tracking of the substrate
- Optimization of roller configurations and material interactions through comprehensive modeling of mechanical behavior and material properties
- Implementation of novel dancer configurations, including pendular and rotary designs, to minimize vibration and maximize stability during high-speed production.
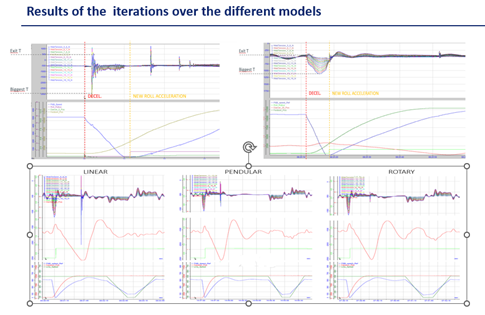
Key findings and results: Through extensive experimentation and analysis, several key findings emerged, demonstrating the efficacy of the new Tension-Control System in improving production efficiency and product quality. These findings include:
- Significant reduction in web-tension increments, leading to enhanced substrate integrity and reduced waste
- Minimization of wrinkles and defects through optimized roller configurations and dancer positioning
- Improved process stability and reliability, resulting in higher throughput and reduced downtime.
The aforementioned outlined approach to the “Digital Twin solution for wrinkle elimination” is a pivotal aspect that entails a hybrid methodology combining real-world data collection via test benchtop operations and digital simulation. This integrated approach is crucial for pinpointing the critical parameters within the process and understanding the material constraints involved.
Implementation and impact: The final implementation of the Tension-Control System represents a culmination of iterative design, rigorous testing and validation. Its deployment in production environments is poised to deliver tangible benefits to producers and OEMs, including:
- Enhanced production efficiency and yield through precise web-handling control and reduced material waste
- Improved product quality and consistency, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and brand reputation
- Increased operational flexibility and adaptability to evolving market demands, ensuring sustained competitiveness in the packaging-material industry.
Conclusion
The packaging-material industry stands at the forefront of innovation, driven by the relentless pursuit of efficiency and precision. In this ever-evolving landscape, Digital Twin technology has emerged as a way to revolutionize how companies approach product development and production optimization.
This article explored the transformative impact of Digital Twin technology on web-handling control, addressing challenges, opportunities and practical applications from continuous web supply to precise tension control and wrinkle elimination. In conclusion, Digital Twin technology represents a paradigm shift in the packaging-material industry, empowering companies to innovate, adapt and thrive in the marketplace. As companies continue to embrace digital transformation, the potential for further advancements and industry-wide benefits is boundless.
Resources
- Industry 4.0: Digital transformation in manufacturing | McKinsey: This article discusses how leading manufacturers are realizing significant value from data and analytics, AI, and machine learning. www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/operations/our-insights/capturing-the-true-value-of-industry-four-point-zero
- How six companies are using technology and data to transform themselves | McKinsey: This article provides insights into how companies are accelerating digitization and the impact on their business models. www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/how-six-companies-are-using-technology-and-data-to-transform-themselves
- Research on Digital Transformation and Organizational Innovation of …: This research paper discusses the impact of digital transformation on manufacturing firms. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13132-023-01703-0
- The practical impact of digital manufacturing: This report discusses the practical impacts of digital manufacturing based on recent international experiences. www.ciip.group.cam.ac.uk/reports-and-articles/the-practical-impact-of-digital-manufacturing/
- Exploring the mechanism of digital technology affordance on …: This study explores the role of digital business capability and organizational legitimacy in the digital transformation of manufacturing enterprises. www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/EJIM-01-2023-0103/full/html
Iñaki Senar Zuñiga, paper converting sales director with MTorres, (Pamplona, Spain), holds a Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical Engineering from Universidad Pública de Navarra. His career began at Schindler, where he advanced from Service Leader to Existing Installation Manager to Branch Manager. Iñaki joined MTorres in 2018 as Service Director, and since 2020, he has been paper converting sales director, responsible for driving sales and expanding market presence. He also has collaborated with various organizations, such as Cámara de Comercio de Pais Vasco and ADD (Assn. for Directors Development) as a consultant for Sales Management courses. Iñaki can be reached at +34-948-317-811, email: inaki.senar@mtorres.com, www.mtorres.com.

